Tiếng Anh 12 Unit 8 ListeningEndangered species 1. Work in pairs. Look at the pictures and discuss the following questions. 2. Choose the correct meanings of the underlined words and phrases. 3. Listen to a talk and choose the correct answer A, B, or C. 4. Listen to the talk again and complete the notes. Use ONE word or a number for each gap. 5. Work in pairs. Discuss the following questions. Quảng cáo
Lựa chọn câu để xem lời giải nhanh hơn
Bài 1 Endangered species (Những loài có nguy có bị tuyệt chủng) 1. Work in pairs. Look at the pictures and discuss the following questions. (Làm việc theo cặp. Quan sát các bức tranh và thảo luận các câu hỏi sau.) What is happening to the tigers in the pictures? What can we do to protect the tigers? (Điều gì đang xảy ra với những con hổ trong tranh? Chúng ta có thể làm gì để bảo vệ loài hổ?)
Lời giải chi tiết: The tigers in the picture are being hunted and kept in a cage. We can stop poaching and release them to protect them. (Những con hổ trong hình đang bị săn bắt và nhốt trong chuồng. Chúng ta có thể ngừng săn bắt và thả chúng ra để bảo vệ chúng.) Bài 2 2. Choose the correct meanings of the underlined words and phrases. (Chọn nghĩa đúng của các từ, cụm từ được gạch chân.) 1. Natural habitats have been degraded by human activity. A. made worse in quality B. made endangered 2. Forest clearance to meet other land needs can destroy the natural habitats of many species. A. removing broken trees B. cutting down trees and other plants 3. Reducing the demand for wild animal parts can help stop poaching. A. the need or desire for particular goods B. things that someone forces you to do 4. Animals bred in captivity would probably not survive if they were released into the wild. A. born while being kept in special facilities B. born while living in the forest Lời giải chi tiết:
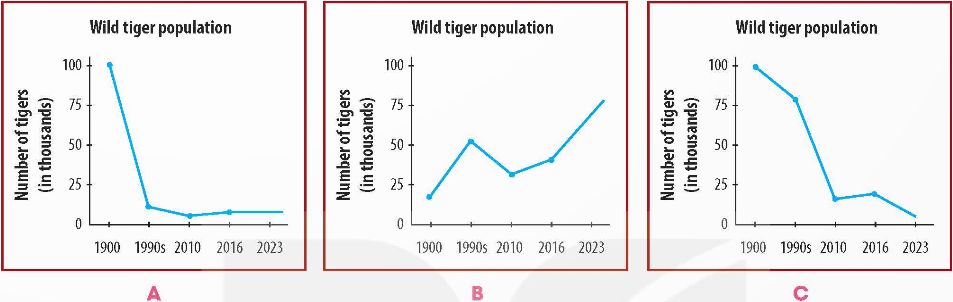
1. A Natural habitats have been degraded by human activity. (Môi trường sống tự nhiên bị suy thoái do hoạt động của con người.) A. made worse in quality (làm cho chất lượng tệ hơn) B. made endangered (làm cho có nguy cơ tuyệt chủng) 2. B Forest clearance to meet other land needs can destroy the natural habitats of many species. (Phá rừng để đáp ứng các nhu cầu đất khác có thể phá hủy môi trường sống tự nhiên của nhiều loài.) A. removing broken trees (loại bỏ cây gãy) B. cutting down trees and other plants (chặt cây và các loại cây khác) 3. A Reducing the demand for wild animal parts can help stop poaching. (Giảm nhu cầu về các bộ phận của động vật hoang dã có thể giúp chấm dứt nạn săn trộm.) A. the need or desire for particular goods (nhu cầu hoặc mong muốn về hàng hóa cụ thể) B. things that someone forces you to do (những điều mà ai đó buộc bạn phải làm) 4. A Animals bred in captivity would probably not survive if they were released into the wild. (Động vật được nuôi nhốt có thể sẽ không thể sống sót nếu chúng được thả vào môi trường tự nhiên hoang dã.) A. born while being kept in special facilities (sinh ra trong khi được giữ ở nơi đặc biệt) B. born while living in the forest (sinh ra khi sống trong rừng) Bài 3 3. Listen to a talk and choose the correct answer A, B, or C. (Nghe một bài nói chuyện và chọn câu trả lời đúng A, B hoặc C.) 1. What is the talk mainly about? A. Threats facing tigers. B. Ways to protect tigers. C. The world's tiger population. 2. Which line graph shows the population of tigers over the past 100 years?
3. As their habitats become smaller, tigers _____. A. look for food in forests B. enter farmers' houses C. attack farm animals 4. What have the tiger breeding farms led to? A. The creation of conservation centres. B. An increase in poaching. C. A decrease in the use of tiger parts. Phương pháp giải: Bài nghe: As part of our series on wildlife, I'm going to talk about tigers today. First, let's take a look at the current situation. Over the last 100 years, the world's wild tiger population has declined significantly. At the beginning of the 20th century, there were 100,000 tigers in the wild. From an estimated 7,000-8,000 in the late 1990s, wild tiger numbers decreased by more than half in 2010. For the first time in 2016, there was a slight increase. However, there were still only about 4,500 wild tigers around the world in 2023. So, why are tigers endangered? What are the threats facing wild tigers? First, tigers have lost a large part of their natural habitats. Their habitats have been destroyed or degraded by human activity. Forest clearance for agriculture and wood, as well as the building of roads and housing have forced tigers to survive in small, unnatural environments. As their habitats become smaller, they find it hard to find food. So they are forced to enter villages and attack farm animals, which often results in killing the tigers by the farmers. However, the most serious threat facing tigers today is poaching and the illegal trade in tiger parts. Historically, tigers were poached for their skins used to make fur coats and home decorations. In addition, there is still demand for their bones, teeth, and other body parts, which are used to make traditional medicines. Nowadays, many people still believe tiger medicines can cure diseases although this has been proven to be wrong by scientists. The demand for tiger parts led to the creation of tiger breeding farms where tigers are bred in captivity and killed for their parts. These farms were originally set up with tiger conservation in mind, as a way to stop poaching. However, these breeding farms led to an increase in poaching. What can we do to help save tigers? Well, we can... Tạm dịch: Trong loạt bài về động vật hoang dã, hôm nay tôi sẽ nói về loài hổ. Trước tiên, chúng ta hãy cùng xem xét tình hình hiện tại. Trong 100 năm qua, quần thể hổ hoang dã trên thế giới đã giảm đáng kể. Vào đầu thế kỷ 20, có 100.000 con hổ hoang dã. Từ con số ước tính 7.000-8.000 con vào cuối những năm 1990, số lượng hổ hoang dã đã giảm hơn một nửa vào năm 2010. Lần đầu tiên vào năm 2016, số lượng hổ hoang dã đã tăng nhẹ. Tuy nhiên, vẫn chỉ có khoảng 4.500 con hổ hoang dã trên toàn thế giới vào năm 2023. Vậy, tại sao hổ lại bị đe dọa? Những mối đe dọa mà hổ hoang dã phải đối mặt là gì? Đầu tiên, hổ đã mất đi phần lớn môi trường sống tự nhiên của chúng. Môi trường sống của chúng đã bị phá hủy hoặc xuống cấp do hoạt động của con người. Việc phá rừng để làm nông nghiệp và khai thác gỗ, cũng như việc xây dựng đường sá và nhà ở đã buộc hổ phải sinh tồn trong những môi trường nhỏ, không tự nhiên. Khi môi trường sống của chúng trở nên nhỏ hơn, chúng thấy khó tìm thức ăn. Vì vậy, chúng buộc phải vào làng và tấn công động vật trang trại, điều này thường dẫn đến việc nông dân giết chết hổ. Tuy nhiên, mối đe dọa nghiêm trọng nhất mà hổ phải đối mặt ngày nay là nạn săn trộm và buôn bán trái phép các bộ phận của hổ. Theo truyền thống, hổ bị săn trộm để lấy da dùng làm áo khoác lông và đồ trang trí nhà cửa. Ngoài ra, vẫn còn nhu cầu về xương, răng và các bộ phận cơ thể khác của chúng, được sử dụng để làm thuốc truyền thống. Ngày nay, nhiều người vẫn tin rằng thuốc hổ có thể chữa khỏi bệnh mặc dù các nhà khoa học đã chứng minh rằng điều này là sai. Nhu cầu về các bộ phận của hổ đã dẫn đến việc thành lập các trang trại nhân giống hổ, nơi hổ được nhân giống trong điều kiện nuôi nhốt và bị giết để lấy các bộ phận của chúng. Các trang trại này ban đầu được thành lập với mục đích bảo tồn hổ, như một cách để ngăn chặn nạn săn trộm. Tuy nhiên, các trang trại nhân giống này đã dẫn đến sự gia tăng nạn săn trộm. Chúng ta có thể làm gì để cứu hổ? Vâng, chúng ta có thể... Lời giải chi tiết: 1. A What is the talk mainly about? (Cuộc nói chuyện chủ yếu nói về điều gì?) A. Threats facing tigers. (Những mối đe dọa đối với loài hổ.) B. Ways to protect tigers. (Cách bảo vệ hổ.) C. The world's tiger population. (Quần thể hổ trên thế giới.) Thông tin: - First, tigers have lost a large part of their natural habitats. (Đầu tiên, loài hổ đã mất đi phần lớn môi trường sống tự nhiên của chúng.) - However, the most serious threat facing tigers today is poaching and the illegal trade in tiger parts. (Tuy nhiên, mối đe dọa nghiêm trọng nhất mà loài hổ phải đối mặt hiện nay là nạn săn trộm và buôn bán trái phép các bộ phận của hổ.) 2. A Which line graph shows the population of tigers over the past 100 years? (Đồ thị nào thể hiện số lượng hổ trong 100 năm qua?)
Thông tin: Over the last 100 years, the world's wild tiger population has declined significantly. At the beginning of the 20th century, there were 100,000 tigers in the wild. From an estimated 7,000-8,000 in the late 1990s, wild tiger numbers decreased by more than half in 2010. For the first time in 2016, there was a slight increase. However, there were still only about 4,500 wild tigers around the world in 2023. (Trong 100 năm qua, quần thể hổ hoang dã trên thế giới đã giảm đáng kể. Vào đầu thế kỷ 20, có 100.000 con hổ trong tự nhiên. Từ con số ước tính 7.000-8.000 vào cuối những năm 1990, số lượng hổ hoang dã đã giảm hơn một nửa vào năm 2010. Lần đầu tiên vào năm 2016, đã có sự gia tăng nhẹ. Tuy nhiên, vẫn chỉ có khoảng 4.500 con hổ hoang dã trên toàn thế giới vào năm 2023.) 3. C As their habitats become smaller, tigers _____. (Khi môi trường sống của chúng trở nên nhỏ hơn, hổ _____.) A. look for food in forests (tìm kiếm thức ăn trong rừng) B. enter farmers' houses (vào nhà nông dân) C. attack farm animals (tấn công động vật trang trại) Thông tin: As their habitats become smaller, they find it hard to find food. So they are forced to enter villages and attack farm animals, which often results in killing the tigers by the farmers. (Khi môi trường sống của chúng trở nên nhỏ hơn, chúng thấy khó tìm thức ăn. Vì vậy, chúng buộc phải vào làng và tấn công động vật trang trại, điều này thường dẫn đến việc những người nông dân giết chết hổ.) 4. B What have the tiger breeding farms led to? (Các trang trại nuôi hổ đã dẫn đến kết quả gì?) A. The creation of conservation centres. (Việc thành lập các trung tâm bảo tồn.) B. An increase in poaching. (Sự gia tăng nạn săn bắt.) C. A decrease in the use of tiger parts. (Giảm việc sử dụng các bộ phận của hổ.) Thông tin: These farms were originally set up with tiger conservation in mind, as a way to stop poaching. However, these breeding farms led to an increase in poaching. (Những trang trại này ban đầu được thành lập với mục đích bảo tồn hổ, như một cách để ngăn chặn nạn săn trộm. Tuy nhiên, những trang trại nhân giống này đã dẫn đến sự gia tăng nạn săn trộm.) Bài 4 4. Listen to the talk again and complete the notes. Use ONE word or a number for each gap. (Nghe lại bài nói và hoàn thành phần ghi chú. Sử dụng MỘT từ hoặc một số cho mỗi chỗ trống.)
Lời giải chi tiết:
Bài 5 5. Work in pairs. Discuss the following questions. (Làm việc theo cặp. Thảo luận các câu hỏi sau đây.) Which threats are facing tigers in Viet Nam? Which one is the most serious? (Những mối đe dọa nào đang đối mặt với hổ ở Việt Nam? Cái nào là nghiêm trọng nhất?) Lời giải chi tiết: Some threats tigers in Viet Nam are facing: poaching, the illegal wildlife trade and habitat loss…. I think poaching is likely the most serious threat. Poachers kill tigers for their body parts. Skins and other parts are also used in traditional medicine or decorative items. (Một số mối đe dọa mà hổ ở Việt Nam đang phải đối mặt: săn bắt, buôn bán động vật hoang dã bất hợp pháp và mất môi trường sống…. Tôi nghĩ nạn săn bắt có thể là mối đe dọa nghiêm trọng nhất. Những kẻ săn bắt giết hổ để lấy các bộ phận cơ thể của chúng. Da và các bộ phận khác cũng được sử dụng trong y học cổ truyền hoặc các vật dụng trang trí.)
|
||||||||||||||||




















Danh sách bình luận