Giải SGK, SBT Unit 3. Việt Nam on the go English Discovery
Giải SGK, SBT Unit 3. Việt Nam on the go English Discovery
2 3.01 Study the Vocabulary box. Match the words with the photos (A-H). Listen and check.
(Nghiên cứu hộp Từ vựng. Nối các từ với các bức ảnh (A-H). Nghe và kiểm tra.)
|
Vocabulary Aspects of our nation (Từ vựng) (Các khía cạnh của đất nước chúng ta) |
|
economic growth increased infrastructure love for nature improved living conditions advanced technology traditional cuisine national identity family values |

Tạm dịch:
economic growth: tăng trưởng kinh tế
increased infrastructure: cơ sở hạ tầng tăng cường
love for nature: tình yêu dành cho thiên nhiên
improved living conditions: điều kiện sống được cải thiện
advanced technology: công nghệ tiên tiến
traditional cuisine: ẩm thực truyền thống
national identity: bản sắc dân tộc
family values: những giá trị gia đình
4 Complete the sentences with the following expressions.
(Hoàn thành các câu với các cách diễn đạt sau.)
|
Vocabulary Expressions of comparison and contrast |
|
similar to …, (tương tự như…,) different from …, (khác với …,) (Tương tự,) In contrast, (Ngược lại,) (Trái ngược với) both ... and … |
1 Nam’s traditional cuisine is similar to different from other Asian cuisines.
2 other ASEAN countries who exprienced a fall in tourist numbers, Vietnam's has made life much less difficult increased infrastructure has made it easier for people to travel around the country.
3 other ASEAN countries who exprienced a fall in tourist numbers, Vietnam's tourism industry has recorded an impressive number of tourists after the COVID-19 pandemic.
4 some other developing countries, Nam’s family values have not changed much over the past century.
5 Today Nam is 30 years ago because of the improved living conditions of its people.
6 Although cities are growing with less green space, the love for nature of people today
is that in the past.
3 Read the Grammar box and find examples of clauses of reason from the dialogue.
(Đọc khung Ngữ pháp và tìm ví dụ về các mệnh đề lý do trong đoạn hội thoại.)
|
Grammar Clauses of reason (ngữ pháp) (Mệnh đề lý do) |
|
• Clauses of reason show the reason why something happened due to the action of the main clause. (Mệnh đề lý do thể hiện lý do tại sao sự việc lại xảy ra do hành động của mệnh đề chính.) (Vì tuần trước chúng tôi đi trung tâm mua sắm nên hôm qua chúng tôi ở nhà.) (Vì quá xa để đi du lịch nên năm nay chúng tôi đã không đến thăm anh em họ hàng của mình.) (Tôi không ăn tối vì tôi không đói.) (Chúng ta có thể viết lại mệnh đề lý do bằng cách sử dụng Because of / Owing to / Due to + N) |
5 Class survey. Interview your friends.
(Khảo sát lớp. Phỏng vấn bạn bè của bạn.)
|
No (Số) |
Name (Tên) |
Questions (Câu hỏi) |
Reasons (Lý do) |
|
1 |
Do you like wearing uniforms to schools? (Bạn có thích mặc đồng phục đến trường không?) |
||
|
2 |
Do you like wearing socks and shoes on hot summer days? (Bạn có thích đi tất và giày vào những ngày hè nóng nực không?) |
||
|
3 |
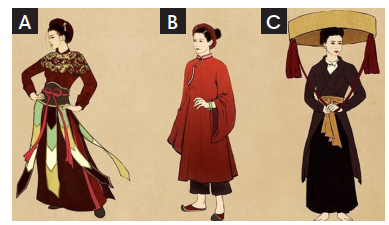
Do you like wearing Áo dài on national days? (Bạn có thích mặc áo dài ngày quốc khánh không?) |
3 Read the Speaking box. Find expressions for comparing ideas in the dialogue.
(Đọc phần Nói. Tìm cách diễn đạt để so sánh các ý trong đoạn hội thoại)
|
Speaking Expressions for comparing ideas and giving opinions (Nói) (Các cách diễn đạt để so sánh ý tưởng và đưa ra quan điểm) |
|
Expressions for comparing ideas This house is smaller than that house. (Ngôi nhà này nhỏ hơn ngôi nhà kia.) (Nhà tôi thuận tiện hơn nhà bạn.) (Nhà này xây bằng gạch, nhà kia làm bằng rơm.) (Cung điện này khác với cung điện đó về kiến trúc.) (Biểu đạt để đưa ra ý kiến) (Tôi nghĩ rằng người dân địa phương nên bảo vệ những ngôi nhà cổ ở khu vực này.) (Tôi tin rằng ngôi nhà này cần được sửa chữa.) (Tôi cảm thấy rằng chúng ta cần phải bảo vệ những ngôi nhà cũ.) |
4 3.07 Listen and repeat.
(Lắng nghe và nhắc lại.)
|
/eə/ |
/əʊ/ |
/ʊə/ |
|
whereas (trong khi) (mặc) (ở đó) |
growth (sự phát triển) (biết) (theo) |
tourist (du khách) (nghèo) (cam đoan) |
5 3.08 Listen and put the words into the correct column.
(Nghe và đặt các từ vào đúng cột.)
|
sure jury compare careful boat share tournament pair toe though |
Tạm dịch:
sure: chắc chắn
jury: bồi thẩm đoàn
compare: so sánh
careful: cẩn thận
boat: thuyền
share: chia sẻ
tournament: giải đấu
pair: đôi
toe: ngón chân
though: mặc dù
|
/eə/ |
/əʊ/ |
/ʊə/ |
2. Match the phrases on the left with their definitions on the right.
(Nối các cụm từ bên trái với định nghĩa của chúng ở bên phải.)
|
1. ☐ Love for nature |
a. positive changes in the quality of life |
|
2. ☐ Traditional cuisine |
b. expansion of production and consumption |
|
3. ☐ Family values |
c. shared values and characteristics of a nation’s people. |
|
4. ☐ Economic growth |
d. affection and appreciation for the natural world |
|
5. ☐ Improved living conditions |
e. food traditions passed down through generations |
3. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate words or phrases below.
(Điền từ hoặc cụm từ thích hợp vào chỗ trống bên dưới.)
|
advanced technology |
increased infrastructure |
traditional cuisine |
|
economic growth |
national identity |
family values |
|
improved living conditions |
love for nature |
1. The _______ of a country leads to more job opportunities for citizens.
2. _______ include better access to healthcare, education, and basic facilities.
3. _______ means that better quality can be seen in transportation, communication, and healthcare systems.
4. _______ such as Al, the Internet, or biotechnology contributes to the overall development of a society.
5. I think you will not lose your _______ if you speak the language, eat the food and communicate with native people.
6. _______ are very important in shaping individuals' characters when they are young.
7. Wherever I go, I will always want to try the country's _______.
8. She spent hours hiking in the mountain. Her _______ was very clear and strong.
1. What are the advantages and disadvantages of travelling by train? Put the following ideas into the right column.
(Ưu điểm và nhược điểm của việc đi tàu hỏa là gì? Hãy xếp những ý sau vào cột bên phải.)
|
reliable |
exhausting |
risk of theft |
affordable |
no door-to-door services |
faster |
|
train problems |
environmentally friendly |
noisy neighbours |
comfortable |
time to relax |
limited destinations |
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
3. Read the article again. Mark the sentences T (true) or F (false).
(Đọc lại bài viết. Đánh dấu các câu T (đúng) hoặc F (sai).)
|
1. The 1,600 km railway route connects various provinces from the north to the south. |
_______ |
|
2. The railway system in Việt Nam is now unable to transport large quantities of goods and passengers. |
_______ |
|
3. The railway system in Việt Nam is known for its low safety and low reliability. |
_______ |
|
4. Rail transport in Việt Nam is the fastest mode of transportation compared to others. |
_______ |
|
5. Travelling by train is not a suitable option for mountainous regions in Việt Nam. |
_______ |
Railway transport was first introduced to Việt Nam during the 1880s. Since then, the railway system has been built and renovated many times. Nowadays, provinces in Việt Nam are connected by the 1,600 km railway route. Super Express trains, which go from the north to the south and vice versa, have been recently introduced to provide more options to passengers.
Since its early operation, the railway system in Việt Nam has offered a great number of benefits. It is well-known for:
- ability to transport large quantities of goods and passengers.
- high safety and reliability in operation and transportation.
- significant contribution to environmental protection by minimizing carbon emissions, noise, and air pollution.
- numerous picturesque locations on the way such as Sa Pa, Huế or Đà Nẵng.
- cost-effectiveness in transporting goods and passengers over long distances.
However, the railway system in Việt Nam also has some disadvantages. Below are some:
- A lack of investment in road infrastructure, equipment, and technology affects the reliability, safety, and transportation time to some extent.
- The limitations in flexibility make it difficult to change transportation routes.
- Travelling by train is slower compared to other modes of transportation.
- Rail transport is not suitable for mountainous terrains. Many provinces in mountainous regions will find it inconvenient to use this mode of transportation.
Despite these limitations, Việt Nam's railway remains an important means in the country's transportation system.
3. Match the clauses on the left with the ones on the right to make meaningful sentences.
(Nối các mệnh đề bên trái với các mệnh đề bên phải để tạo thành câu có nghĩa.)
|
1. ☐As uniforms are compulsory in many schools, |
a. our living conditions have improved. |
|
2. ☐It's easier to travel to far-away cities now |
b. a lot of students wear them daily. |
|
3. ☐Because of my busy schedule, |
c. because of its light silk fabric. |
|
4. ☐Áo dài is well-suited for Việt Nam's hot and humid climate |
d. due to improvements in public transport. |
|
5. ☐Due to economic growth and increased infrastructure in the past decades, |
e. I couldn't join the Áo dài festival last week. |
2. Complete the sentences with the words / phrases given below.
(Hoàn thành các câu bằng các từ/cụm từ cho sẵn bên dưới.)
|
fortune |
entertaining |
historical legends |
pay homage to |
1. In water puppetry, people control the puppets under the water, telling stories, usually about _______ of Việt Nam.
2. In lion dance, people dress up as lions and dance around. It's really _______ to watch.
3. Traditional dances bring joy and _______ to the audience.
4. Through traditional dances, we _______ our traditions and ancestors.
1. Put the words / phrases below next to their meaning.
(Đặt các từ/cụm từ bên dưới theo nghĩa của chúng.)
|
functional |
minimalist |
tile |
courtyard |
tube house |
1. designed to be useful rather than attractive: _______
2. a square or rectangular piece of baked clay used for covering roofs, floors, etc.: _______
3. a house that is narrow and has a lot of floors: _______
4. using only a few materials, colours and simple shapes: _______
5. an area outside with walls around: _______
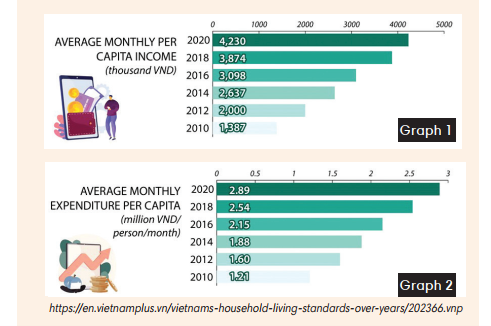
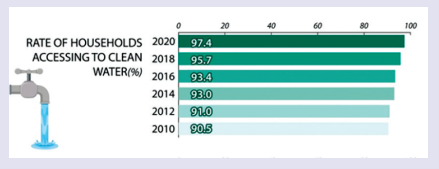
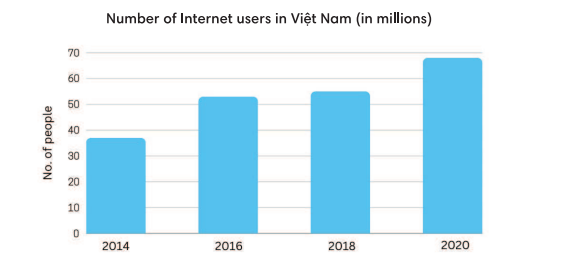
1. Match each part of the report with its function.
(Ghép từng phần của báo cáo với chức năng của nó.)
|
1. ☐ Introduction |
a. Overall, this figure saw a steady increase over the given period. |
|
2. ☐ General trend |
b. Specifically, in 2014, there were just around 4 million Vietnamese families with Internet access, but this number jumped significantly to more than 15 million 6 years later. |
|
3. ☐ Detailed data |
c. The bar chart shows the number of households with Internet access in Việt Nam from 2014 to 2020. |